Writing Effective Jira Prompts: A Practical Guide for ChatGPT and AI Tools
Learn how to structure your questions to get specific, actionable solutions for Jira issues instead of generic troubleshooting advice
Why Most Jira Troubleshooting Takes Hours (Not Minutes)
As Jira administrators, we’ve all been there: an OutOfMemoryError appears, and suddenly you’re deep in Stack Overflow threads from 2019, trying random JVM settings that worked for someone with a completely different setup.
The real problem isn’t the error itself – it’s that we’re asking AI the wrong questions. When you type “Jira OutOfMemory fix” into ChatGPT, you get generic advice that could apply to any Java application. But your Jira instance is unique: specific version, plugin configuration, user count, and workload patterns.
Typical troubleshooting flow:
1. Generic search → “Clear cache and restart Jira”
2. Doesn’t work → Try increasing heap to 8GB (random guess)
3. Still failing → Reading 10-year-old Atlassian community posts
4. Hours later → Finally find someone mentioned checking Metaspace for plugin issues
The difference between a 4-hour debugging session and a 5-minute fix? Giving AI the context it needs to think like a Jira expert, not a generic Java developer. Here’s what changes everything:
With proper context, AI can immediately identify that new plugins exhausted Metaspace (not heap), recommend the exact size increase based on plugin count, and even warn you about specific plugins known for memory leaks in your Jira version.
Building Effective Prompts: The 4-Component Framework
After testing hundreds of prompts with ChatGPT, Claude, and other AI services for Jira troubleshooting, we’ve found that successful prompts consistently follow a simple 4-part structure. This isn’t marketing theory – it’s what actually works in production environments.
The difference between getting “Have you tried restarting?” and getting the exact JVM parameters you need? These four components. Let’s break down each one with real examples from daily Jira administration.
This sets the AI’s knowledge context. Instead of generic IT advice, you get responses from the perspective of someone who understands Jira’s architecture, common issues, and best practices.
Your Jira 9.4 Data Center instance with PostgreSQL has different solutions than someone’s Jira 8.20 Server with MySQL. Specific context prevents generic answers that don’t apply to your setup.
The more specific data you provide, the more accurate the diagnosis. Include error messages, stack traces (even partial), current JVM settings, and when the issue started.
Current: -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=256m
Started: After installing Insight plugin Monday
Users see: 502 gateway timeout after 30 seconds”
Tell the AI exactly what you need: root cause analysis, step-by-step fix, preventive measures, monitoring queries. This prevents lengthy explanations when you need quick commands.
1. Most likely root cause
2. Exact JVM parameters to add
3. SQL query to verify the fix
4. One-line explanation for management”
Pro Tip: Start Simple, Add Detail
You don’t need all four components for every question. Start with role + context for general questions, then add data + output requirements for complex troubleshooting. The key is being specific about YOUR environment, not describing Jira in general.
Putting It Into Practice: A Real Comparison
Let’s see how the 4-component framework transforms a typical support request into a prompt that actually gets results. This is a real scenario from last week’s production incident.
The Key Differences That Matter
- Role: Told AI to think like a Jira performance specialist, not generic IT support
- Context: Specific version, deployment type, and infrastructure details
- Data: Actual metrics and timeline (not just “it’s slow”)
- Output: Requested ranked causes and specific commands (not general advice)
Practical Prompt Templates for Common Jira Issues
Here are battle-tested prompt templates for the most frequent Jira problems. Each template follows the 4-component structure and includes placeholders for your specific data.
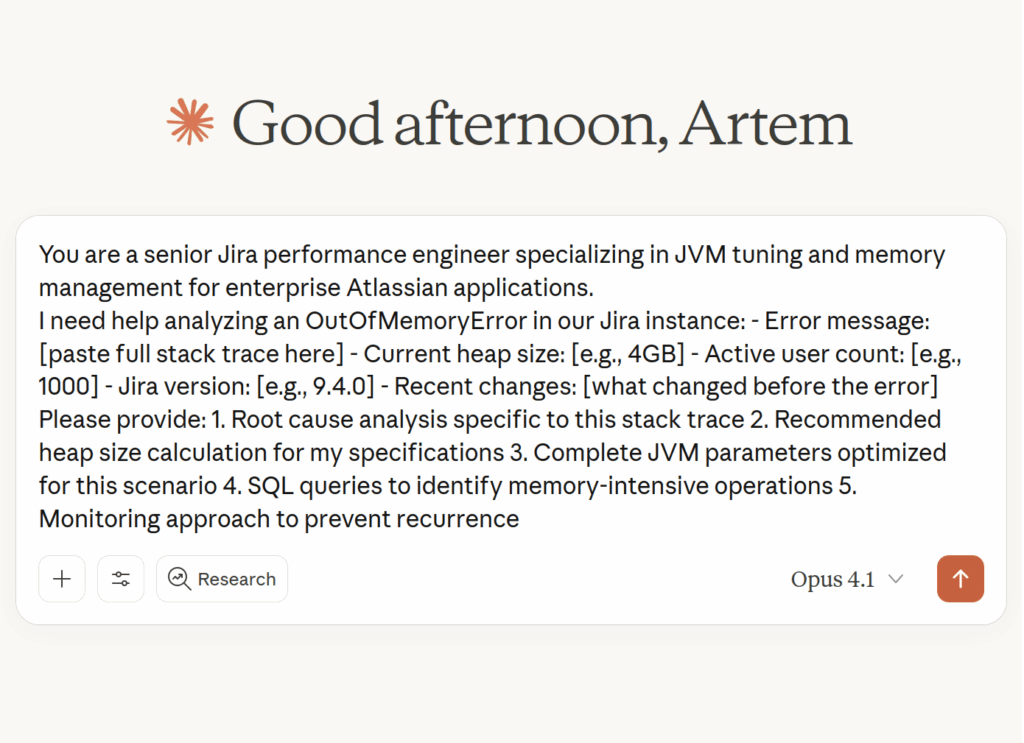
1. OutOfMemoryError Analysis
When Jira crashes with memory errors, this prompt helps identify whether it’s heap, metaspace, or direct memory issues.
You are a senior Jira performance engineer specializing in JVM tuning and memory management for enterprise Atlassian applications.
I need help analyzing an OutOfMemoryError in our Jira instance:
– Error message: [paste full stack trace here]
– Current heap size: [e.g., 4GB]
– Active user count: [e.g., 1000]
– Jira version: [e.g., 9.4.0]
– Recent changes: [what changed before the error]
Please provide:
1. Root cause analysis specific to this stack trace
2. Recommended heap size calculation for my specifications
3. Complete JVM parameters optimized for this scenario
4. SQL queries to identify memory-intensive operations
5. Monitoring approach to prevent recurrence
2. Database Integrity Issues
For constraint violations, orphaned data, or corruption that prevents Jira from starting or functioning properly.
You are a Jira database specialist with deep expertise in AO_ tables, integrity constraints, and Jira’s database schema across different database systems.
Our Jira instance has a database integrity issue:
– Error: [paste exact constraint violation]
– Database type: [PostgreSQL/MySQL/Oracle/MSSQL]
– Affected table: [e.g., AO_60DB71_COLUMN]
– Jira version: [version number]
– When it occurs: [during startup/specific action]
I need:
1. Safe SQL queries to identify the corrupted records
2. Backup procedures before attempting repairs
3. Repair SQL with a rollback strategy
4. Verification queries to confirm the fix
5. Root cause analysis and prevention steps
3. Permission and Access Problems
When users can’t access projects, perform actions, or permissions behave unexpectedly despite correct configuration.
You are a Jira security architect specializing in permission schemes, project roles, and complex authorization scenarios.
We have a permission issue that needs investigation:
– User: [username or group]
– Cannot perform: [specific action like “create issue”]
– In project: [project key]
– Current permissions visible: [what UI shows]
– Expected behavior: [what should happen]
– Authentication method: [LDAP/SAML/local]
Please help with:
1. SQL queries to trace the complete permission inheritance chain
2. All configuration points to check, in order
3. Common issues specific to this permission type
4. Step-by-step fix via UI or database
5. Audit query to find other affected users
4. Performance Degradation
For slow page loads, dashboard timeouts, or gradual performance decline without obvious errors.
You are a Jira Data Center performance specialist with expertise in query optimization, caching strategies, and resource tuning.
Our Jira instance is experiencing performance issues:
– Symptom: [e.g., dashboards take 30+ seconds]
– User count: [concurrent users]
– Infrastructure: [nodes, RAM, CPU]
– Database metrics: [connection pool, query time]
– Started: [gradual or sudden, after what event]
Provide analysis for:
1. Most likely bottlenecks ranked by probability
2. Diagnostic queries and commands for each area
3. Quick wins vs long-term optimizations
4. Specific configuration changes with values
5. Performance baseline metrics to track
Did This Guide Help You?
We’d love to hear about your experience using these prompts. What worked best for your Jira environment? Share your success stories or suggest improvements in the comments below.
Start Using AI for Jira Troubleshooting Today
You now have the framework to turn any Jira problem into a well-structured prompt that gets real solutions. The difference between hours of debugging and minutes of fixing often comes down to how you ask the question.
Tools That Make AI Troubleshooting Even Faster
While AI can solve most Jira problems, getting the right data to feed into your prompts can still take time. If you’re tired of SSH sessions and command-line navigation, tools like Home Directory Browser give you instant UI access to logs, files, and database queries – turning 15-minute data gathering into 30-second clicks.
View on Atlassian Marketplace →